Universal Serial Bus (USB): Key Features, Types, and Uses
2023/11/10 10:08:13
Views:
USB is an essential technology in modern electronics. USB is vital for charging devices and data transfer. This article dives into the key features, types, and uses of USB, along with a detailed look at its software and hardware structure, as well as how USB technology has developed over time.
USB Ports, Cables, Types, & Connectors
- What Does USB Stand For?
- Key Features of USB
- What is a Universal Serial Bus Port?
- Types of USB Connections
- USB Development Over the Years
- Uses of Universal Serial Bus (USB)
- Definition of Universal Serial Bus
- Universal Serial Bus Definition vs. Other Connection Technologies
- Define Universal Serial Bus in Simple Terms
- Future of USB Technology
- Conclusion
- (Frequently Asked Questions) FAQs
-
What Does USB Stand For?
USB stands for Universal Serial Bus.It is a standardized innovation utilized to put through devices like computers, consoles, cameras, and outside drives. The reason for USB is to form information exchange and control conveyance between gadgets basic and widespread, killing the requirement for numerous sorts of cables and ports.

Key Features of USB
USB is known for its adaptability, ease of utilization, and unwavering quality. Underneath are a few of the foremost critical highlights that make USB the go-to association standard for electronic gadgets:
1. Plug-and-Play Compatibility
One of the standout highlights of USB is its plug-and-play usefulness. Clients can basically plug a gadget into a USB port, and it'll be immediately recognized by the framework without requiring extra drivers or program. This includes permits for consistent and effective gadget associations, sparing time, and exertion.
2. Power Delivery
In expansion to data transfer, USB can deliver power to connected devices. Whether it's charging a phone or fueling up peripherals like keyboards and outside difficult drives, USB has finished up being a broad charging standard. USB Power Delivery (PD) indeed permits quick charging in more up-to-date gadgets, giving more control in less time.
3. Universal Compatibility
The primary advantage of USB lies in its universal compatibility. This compatibility makes USB the standard choice for data transfer and power delivery between electronic devices.
4. Multiple Speed Standards
Over the long time, USB innovation has progressed in terms of speed. USB 2.0, USB 3.0, and USB 3.1 offer powerfully speedier data trade rates. The foremost later standard, USB 4.0, gives indeed more prominent speed and usefulness, permitting for speedier record exchanges and more vigorous network alternatives.
What is a Universal Serial Bus Port?
A Universal Serial Bus port is the physical interface that allows USB devices to connect to a computer or another device. The harbor is planned to oblige the USB connector, empowering both information transmission and control supply. You'll discover USB ports on about each cutting-edge electronic gadget, including tablets, desktop computers, amusement comforts, and indeed vehicles.
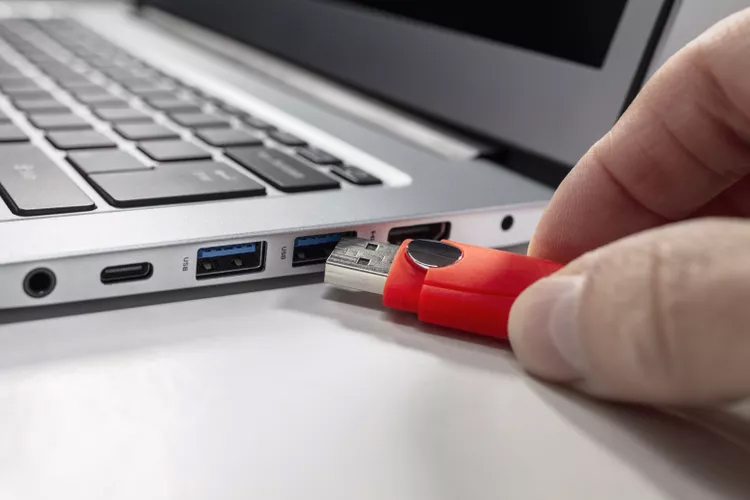

USB Hardware Structure
The hardware structure of USB is designed to be simple yet highly functional. It consists of several key components that allow for data transfer, power delivery, and device recognition. These include:
● USB Host Controller: This component is capable for overseeing the information stream between associated gadgets and the framework. It is ordinarily built into the motherboard of computers or inserted in other gadgets.
● USB Center: A USB center permits different gadgets to be associated through a single harbor. Numerous cutting-edge computers and docking stations utilize center points to back numerous gadgets at the same time.
● USB Cables and Connectors: The genuine cables and connectors are significant parts of the equipment structure. As talked about previously, USB comes in numerous sorts (Type-A, Type-B, Type-C) depending on the gadget and the level of data transfer required.
● USB Gadget: The gadget associated with USB, such as a console, mouse, or outside capacity, shapes the endpoint within the equipment structure. These devices rely on the USB protocol to communicate with the host.
The hardware design of USB makes it robust, ensuring reliable connectivity even in harsh environments or with frequent use.
USB Software Structure
The software structure of USB is equally important, as it enables seamless communication between the hardware and the system. The USB software stack includes several layers:
● USB Driver: Each device type connected via USB requires a driver to function correctly. Whereas numerous drivers are pre-installed on working frameworks (e.g., Windows, macOS, Linux), a few gadgets may require extra drivers introduced.
● Host Controller Driver (HCD): This driver oversees the interface between the have framework and the USB equipment controller. It guarantees information is sent to and gotten from the right gadget.
● USB Protocol Layer: The convention layer guarantees that information transmission follows the USB standard. It characterizes how gadgets communicate with each other, guaranteeing compatibility over diverse producers.
● USB Device Stack: Each USB device has its own software stack, which interacts with the host system. The device stack is responsible for understanding requests from the host and responding appropriately.
USB's hardware and software create a standardized communication system, ensuring smooth device operation.
Types of USB Connections
USB technology has evolved, resulting in several types of USB connectors, each with its specific use case. Below is a breakdown of the most common types of USB connections:
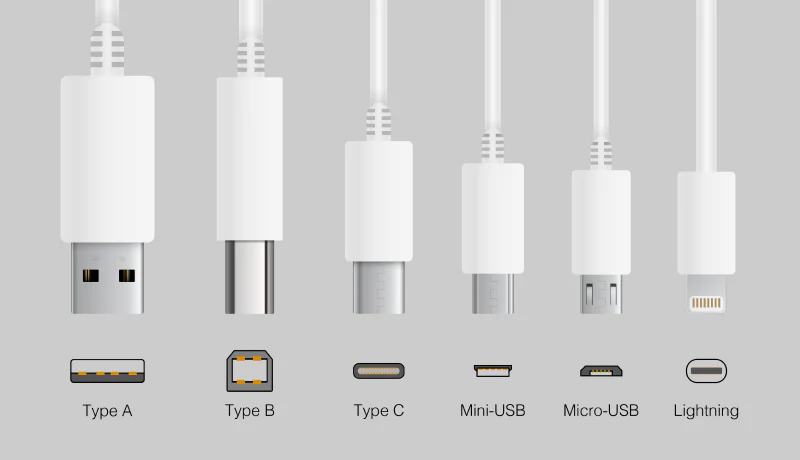

1. USB Type-A
The foremost recognizable sort of USB connector is the USB Type-A. Typically the standard rectangular harbor is found on more seasoned computers, gaming comforts, and a few peripherals. While it has been widely replaced by newer types in modern devices, USB Type-A is still in use for backward compatibility with older equipment.
2. USB Type-B
USB Type-B is less common and is regularly utilized for interfacing printers and other bigger peripherals to a computer. The Type-B connector is square-shaped and bigger than the Type-A.
3. USB Type-C
USB Type-C has rapidly become the universal connector for advanced gadgets. It is reversible, which suggests you'll be able to plug it in either way, and underpins much quicker data transfer speeds compared to older types. USB Type-C moreover conveys higher control for charging gadgets, making it a favorite for smartphones, tablets, and tablets.
4. Mini-USB
Mini-USB is an older USB connector commonly used in early digital cameras, MP3 players, and older mobile devices. It is smaller than standard USB Type-A and Type-B connectors but slightly larger than Micro-USB. Today, Mini-USB is rarely found in modern devices as it has largely been replaced by Micro-USB and USB Type-C.
5. Micro-USB
Micro-USB is a smaller, upgraded adjustment of Mini-USB and was broadly utilized in more prepared smartphones, tablets, chargers, and other convenient gadgets. Whereas it is still shown in a number of contraptions, most progressed contraptions have transitioned to USB Type-C, which offers speedier data trade speeds and more vital control delivery.
6. Lightning
Lightning may be an exclusive connector created by Apple for its gadgets, including iPhones, iPads, and iPods. Littler and simple to utilize, Lightning connectors can be embedded in either introduction, similar to USB Type-C. However, it is selected for the Apple biological system and is not consistent with other sorts of USB connections.
USB Development Over the Years
USB headway began within the 1990s when a consortium of tech companies, including Intel, Microsoft, and IBM, pointed to standardized computer ports. Sometime recently USB, interfacing gadgets like printers, mice, and outside capacity to a computer required distinctive sorts of ports and cables, frequently driving to compatibility issues.
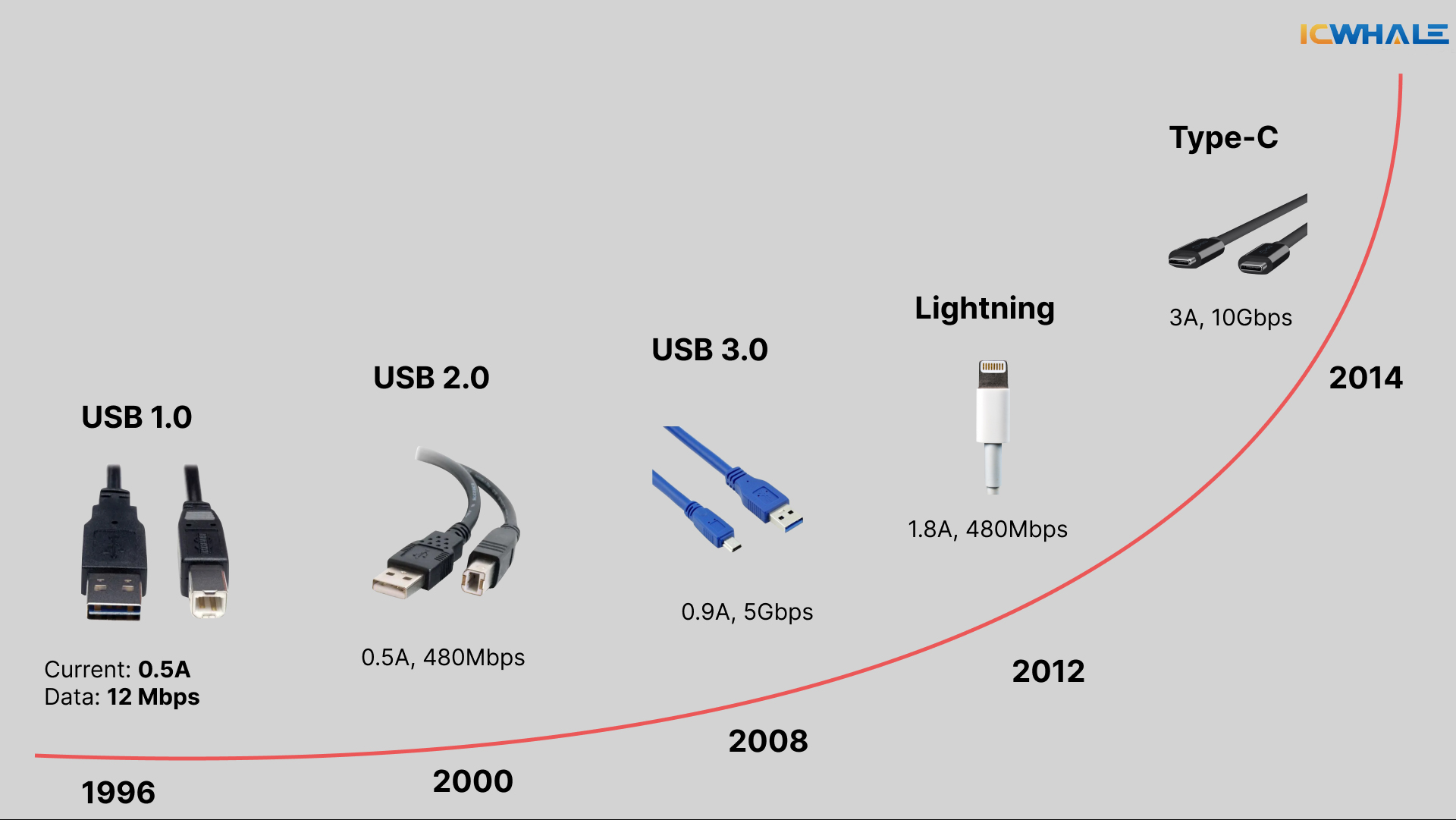
Early Days (USB 1.0)
The essential frame, USB 1.0, was discharged in 1996 and advertised information exchange speeds of up to 12 Mbps with a current of 0.5A. While more often than not directly compared to cutting-edge benchmarks, USB 1.0 was progressive at the time since it rearranged fringe associations, permitting less demanding communication between computers and outside gadgets.
Moved forward Speed and Usefulness (USB 2.0 and 3.0)
With the discharge of USB 2.0 in 2000, information exchange rates expanded altogether to 480 Mbps, too with a current of 0.5A. This made exchanging huge records like recordings and pictures much more proficient. USB 2.0 too moved forward control conveyance, making it more compelling for charging gadgets. By 2008, USB 3.0 presented indeed speedier information exchange speeds of up to 5 Gbps with a current of 0.9A, permitting faster record exchanges and more solid gadget associations.
The Rise of USB Type-C and USB 4.0
USB Type-C, presented in 2014, revolutionized the USB biological system with its reversible plan and moved forward control conveyance, supporting up to 3A of current. It offers information exchange speeds of up to 10 Gbps, making it a favored connector for present-day gadgets. USB 4.0, the most recent emphasis, pushes this indeed encourage with speeds of up to 40 Gbps and compatibility with Thunderbolt 3, supporting numerous information streams and progressed network highlights.
Uses of Universal Serial Bus (USB)
USB serves various purposes within the tech world, making it an unimaginably flexible innovation. A few of the essential employments incorporate:
1. Information Transfer
One of the initial capacities of USB is exchanging information between gadgets. Whether you're moving records from a smartphone to a laptop or interfacing an outside difficult drive, USB makes the method quick and simple. The most recent USB measures offer information exchange rates that can handle indeed expansive records like HD recordings and high-resolution pictures.
2. Charging Gadgets
Another imperative utilize of USB is charging. From smartphones to convenient batteries, USB provides a helpful way to charge gadgets. USB Control Conveyance (PD) presented quick charging capabilities, altogether lessening device charging time.
3. Interfacing Peripherals
USB is commonly utilized to put through peripherals like consoles, mice, printers, and outside difficult drives to computers. The plug-and-play usefulness guarantees these gadgets work consistently without the require for complex setup strategies.
4. Sound and Video Transmission
In later a long time, USB has extended past information and control conveyance to incorporate sound and video transmission. For illustration, USB Type-C can presently be utilized to transmit video signals, making it a viable alternative to HDMI in a few cases. This permits cleaner setups and diminishes the number of cables required for interfacing numerous gadgets.
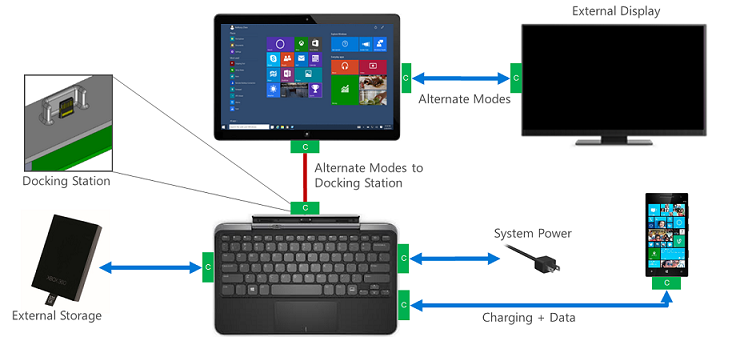
Demonstrates how USB connects multiple devices such as external storage, game controllers, and keyboards
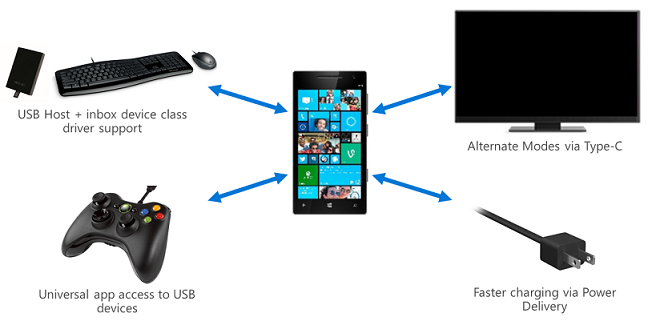
Shows USB docking station connections for data transmission and device charging
Definition of Universal Serial Bus
The definition of Universal Serial Bus (USB) is a standardized connection technology used to link electronic devices for data transfer and power delivery. USB was created within the mid-1990s as a way to streamline the method of interfacing different sorts of peripherals to computers and other electronic gadgets. Nowadays, USB remains a key innovation in both individual and proficient situations.
Universal Serial Bus Definition vs. Other Connection Technologies
USB is not the only connection standard available, but it has significant advantages over other methods, like FireWire, Thunderbolt, and HDMI. Here's how USB stacks up against these alternatives:
1. USB vs. FireWire
FireWire, once considered a competitor to USB, is present to a great extent out of date. Whereas it advertised speedier information exchange speeds during its time, USB 3.0 and USB 4.0 have since outperformed it, making USB the more flexible and far-reaching choice.
2. USB vs. Thunderbolt
Thunderbolt is a high-speed data transfer technology primarily found in high-end gadgets. Whereas Thunderbolt offers faster data rates, it is less commonly utilized and more costly than USB. USB Type-C, with its expanded speed and control capabilities, is presently catching up to Thunderbolt in numerous ranges.
3. USB vs. HDMI
USB is mainly used for data transfer and charging, while HDMI is specifically for transmitting video and audio signals. However, USB Type-C is capable of handling video output, making it a more versatile choice for modern devices, particularly when connecting laptops to monitors or TVs.
Define Universal Serial Bus in Simple Terms
In basic terms, USB is a universal system that allows different electronic devices to communicate and share data. It has made it conceivable for individuals to utilize one standard cable for different assignments, whether connecting a keyboard to a computer or charging a smartphone.
Future of USB Technology
As innovation progresses, USB proceeds to advance. The presentation of USB 4.0 offers quicker speeds and greater power capabilities, guaranteeing that it remains the standard for interfacing gadgets. Looking ahead, USB will likely proceed to play a critical role in data transfer,, charging, and indeed video transmission, all while keeping up its trademark ease of utilization.
Conclusion
In conclusion, USB remains an essential technology for connecting and powering devices, with its universal compatibility and ongoing evolution ensuring its place in modern technology for years to come.
(Frequently Asked Questions) FAQs
What is the purpose of a Universal Serial Bus USB on a laptop or desktop computer?
The primary purpose of a The essential reason USB port on a laptop or desktop is to empower the simple association between the computer and outside gadgets. Whether for data transfer, power delivery, or interfacing peripherals like printers, capacity drives, or input gadgets, USB streamlines these associations. is to enable easy connection between the computer and external devices. Whether for data transfer, control conveyance, or interfacing peripherals like printers, capacity drives, or input gadgets, USB disentangles these associations.What is the difference between parallel port and Universal Serial Bus?
The key difference is that a The key capability is that a parallel harbor exchanges particular bits of information at the same time, whereas a USB exchanges information serially, one bit at a time. In showing disdain toward this, USB is much faster and more viable than more prepared parallel harbor development, which is by and by for the most part out of date. exchanges information serially, one bit at a time. In spite of this, USB is much quicker and more effective than more seasoned parallel harbor innovation, which is presently generally out of date.Is Universal Serial Bus a storage device?
No, USB is a connection standard, not a storage device. However, it can connect storage devices like flash drives and external hard drives.Is Universal Serial Bus an input or output device?
USB is an association standard, facilitating both input and yield gadgets to put through with computers.Is USB 2.0 the same as USB-C?
No, USB 2.0 alludes to an adaptation of the standard, whereas USB-C may be a sort of physical connector. USB-C connectors can back different interface conventions, counting the 2.0, 3.0, and indeed the 4.0 guidelines, depending on the gadget.What does bus in USB mean?
The term "bus" in Universal Serial Bus refers to a framework that empowers numerous gadgets to communicate through a single information channel, much like travelers sharing space on a transport. It oversees the exchange of information and control between associated gadgets and the framework. alludes to the framework that permits numerous gadgets to communicate over a single information channel, compared to how travelers share space on a transport. It handles the transfer of data and power between the connected devices and the host system.Related Information
-
-
Phone
+86 135 3401 3447 -
Whatsapp





