Types of Transistors: Symbols and Applications
2024/10/24 16:32:01
Views:
Understanding the different types of transistors is crucial because each has a specific purpose in electronic circuits, from amplification to switching and signal modulation. In this article, you will learn about the different types of transistors, their applications, and their symbols.
Transistors, How do they work?
What is a Transistor?
A transistor is a device composed of three layers of semiconductor material, which has the functions of detection, regulation, amplification, switching, voltage regulation and signal modulation. The transistor consists of three parts: emitter, base and collector, and contains two PN junctions.
Types of Transistors

The following are the categories of the main types of transistors:
1. Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)
Bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a common type of transistor, which is divided into NPN type and PNP type.
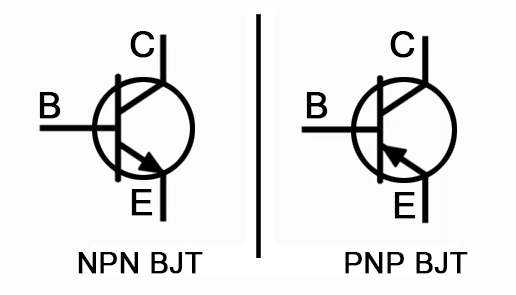
- NPN: When the base receives a positive voltage, current flows from the collector to the emitter. NPN transistors are commonly used in applications such as signal amplification and circuit switching.
- PNP: When the base receives a negative voltage, current flows from the emitter to the collector. They are also used for amplifying and switching circuits, but the polarity is different from the NPN type.
Summary: NPN transistors are on when the base is positive, while PNP transistors are on when the base is negative. Both types are used for signal amplification and circuit switching, with current flowing in opposite directions.
2. Field-Effect Transistors (FET)
BJTS rely on current flow, while Field-Effect Transistor (FETs) control current through an electric field. Fets are commonly used in applications with high input impedance and low power consumption, and are mainly divided into JFET and MOSFETs.
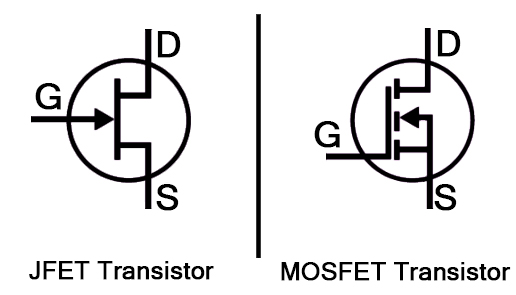
Junction Field-Effect Transistor (JFET) : This type of FET regulates the current between the drain and source by controlling the gate voltage. The gate and channel of JFET form PN junction, and the current in the channel can be controlled by changing the gate voltage.
Insulated Gate Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET) : This is the most common type of FET. MOSFETs have an insulating layer (usually silicon oxide) between the gate and the channel, MOSFETs can achieve efficient switching and amplification operations, low power consumption, and are widely used in various electronic circuits.
3. Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBT)
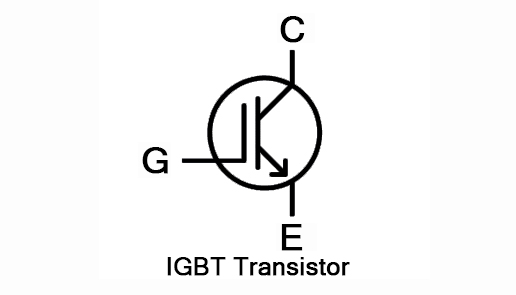
An insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) is a semiconductor device specifically designed for high-voltage, high-current applications. You can use it for motor control, power inverters, and switching power supplies. It combines the fast switching capability of MOSFETs with the high current capability of bipolar transistors, ensuring efficient power management.
4. Darlington Transistors
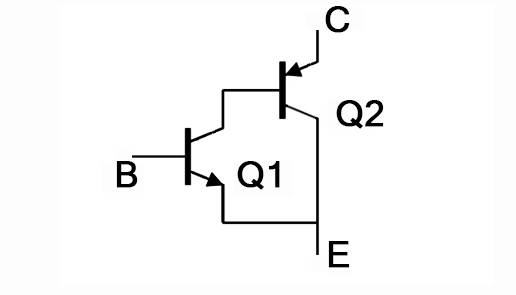
The Darlington transistor is two BJTS connected in series to significantly increase the current gain. It is commonly used in applications that require high current amplification, such as power switches and motor controls.
5. Phototransistor
Phototransistors convert light into electrical signals and are commonly used in sensors and remote controls.
6. Power Transistors

The power transistor is a three-terminal component used to handle high voltage and high current, and realizes amplification and switching operation through the emitter, base and collector, which is usually used in the fields of power control, motor drive and signal amplification.
7. Specialized Transistor Types
A variety of specialized transistors are designed for specific applications:
- Static Induction Transistor (SIT): It is a unipolar device that relies mainly on a few conduction. Its working principle is similar to JFET (junction field effect tube), and the current in the channel is modulated through the electric field to achieve current control.
- High Electron Mobility Transistor (HEMT) : The use of gallium nitride (GaN) and gallium aluminum nitride (AlGaN) heterojunction to provide a channel for charge carriers has faster electron mobility than conventional semiconductors.
- BiMOS Transistors:BiMOS Transistors combine the high-current characteristics of BJT with the high-input impedance and low-power characteristics of MOSFETs, making them especially suitable for fast switching circuits.
- Vertical MOSFETs:Current flows from the source at the bottom of the device to the drain at the top, and its current path is vertical. This design improves efficiency and performance in high-power and high-current applications.
- Dual Gate MOSFETs: Dual-gate MOSFETs have two independently controlled gates to increase switching speed and reduce parasitic effects, and are commonly used in high-frequency circuits.
- GaN and SiC transistors: GaN provides fast switching and low on-resistance for high-frequency use, while SiC can handle high temperatures and high voltages.
Conclusion
Choosing the right transistor depends on the needs of the project, such as current, speed, and efficiency. Understanding the different types of transistors helps you make better choices.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
what does e stand for in transistor?
In a transistor, E stands for Emitter, whose role is to inject charge carriers into the base, which allows current to flow through the transistor.
what does a transistor do?
A transistor controls the flow of current in a circuit. It can amplify signals, switch power or signals as a switch, and modulate currents. The transistor is like a "switch" or "gate" that regulates the electrical signals in the circuit by controlling the voltage to decide whether to allow current through.
How does a transistor work?
The transistor controls the flow of current through the base. When the small current flows into the base, the larger current can flow from the collector to the emitter, so as to achieve amplification or switching function; When there is no current at the base, the transistor is in the off state.
How many transistors in a cpu?
A CPU typically contains more than a billion transistors .
Related Information
-
-
Phone
+86 135 3401 3447 -
Whatsapp





