Lidar and Microwave Radar: Similarities, Differences and Applicable Scenarios
2024/5/7 11:19:47
Views:
Radar technology: analysis of differences and application scenarios between laser and microwave
Radar technology plays a vital role in modern science and technology, especially in fields such as autonomous driving, aerospace, military reconnaissance, and remote sensing mapping. Although LiDAR and microwave radar belong to the same radar family, they have significant differences in principles, performance indicators and application scenarios. This essay will examine the distinctions between lidar and microwave radar, as well as each technology's unique features.
The difference at the principle level
lidar
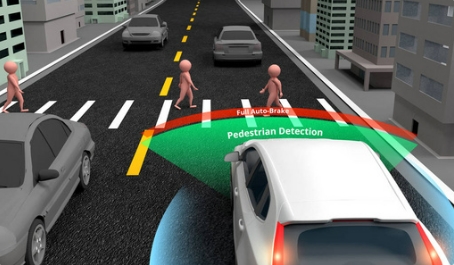
Lidar uses a laser light source to emit very short light pulses. When the light pulse hits the target, it is reflected, and the receiver captures and records part of the reflected light. By measuring the difference in emission and return times of light pulses, the distance to the target is calculated, and the relative speed of the target is determined by analyzing the phase difference of the reflected light. LiDAR has extremely high directivity and angular resolution, allowing it to construct detailed three-dimensional spatial images.
 microwave radar
microwave radar
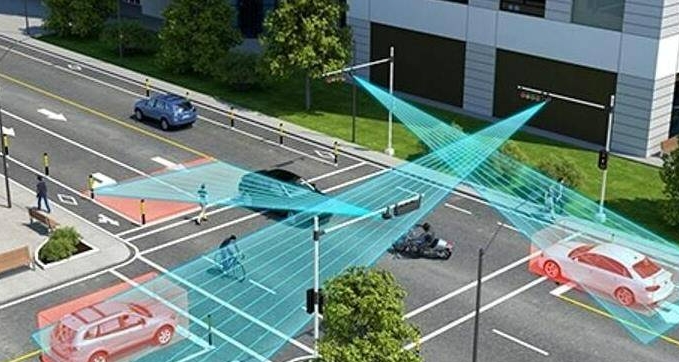
Microwave radar uses electromagnetic waves in the microwave frequency band for detection. It sends continuous or pulsed microwave energy to the surrounding space. When the microwave encounters the target object, it is reflected. The radar receiving system captures the echo signal and changes it according to the arrival time and amplitude of the signal. Determine the distance, bearing and speed of the target. The wavelength of microwave radar is much larger than that of laser, causing its resolution and penetration characteristics to be different from lidar.
 Comparison of performance indicators
Comparison of performance indicators
resolution
LiDAR has extremely high resolution, including distance, angle and speed resolution, and can accurately distinguish very close objects and depict details at the level of several centimeters, making it suitable for areas such as autonomous driving.
The resolution of microwave radar is relatively low, especially the early microwave radar was mainly used for long-distance detection and large-scale coverage. However, with the advancement of technology, its resolution has been improved, but it is still not as good as lidar.
Penetration and weather adaptability
Microwave radar has strong penetrability and can maintain good detection results especially in bad weather. It is suitable for aviation, navigation and other fields.
Lidar will be greatly affected when encountering water droplets, haze, etc., but it has excellent detection performance in clear environments.
Anti-interference and concealment
Due to its short wavelength, lidar has less interference from natural background radiation and has strong anti-reconnaissance capabilities.
Microwave radar may be interfered by radio signals, but the universality of its band gives it a certain ability to resist interference.
Differences in application scenarios
Applications of lidar
Lidar is widely used in fields such as unmanned driving, three-dimensional terrain surveying and construction planning, and has become a key sensor for advanced autonomous driving systems.
Microwave Radar Applications
Microwave radar is widely used in weather forecasting, aviation navigation, automobile safety functions and other fields. Particularly in the area of vehicle safety, millimeter wave radar is becoming more and more common.
LiDAR and microwave radar have their own characteristics in terms of principles, performance and application fields, and each has its own advantages and disadvantages. In practical applications, it is often necessary to comprehensively consider their advantages and disadvantages and select appropriate radar technology to meet different needs.
Radar technology plays a vital role in modern science and technology, especially in fields such as autonomous driving, aerospace, military reconnaissance, and remote sensing mapping. Although LiDAR and microwave radar belong to the same radar family, they have significant differences in principles, performance indicators and application scenarios. This essay will examine the distinctions between lidar and microwave radar, as well as each technology's unique features.
The difference at the principle level
lidar
Lidar uses a laser light source to emit very short light pulses. When the light pulse hits the target, it is reflected, and the receiver captures and records part of the reflected light. By measuring the difference in emission and return times of light pulses, the distance to the target is calculated, and the relative speed of the target is determined by analyzing the phase difference of the reflected light. LiDAR has extremely high directivity and angular resolution, allowing it to construct detailed three-dimensional spatial images.

Microwave radar uses electromagnetic waves in the microwave frequency band for detection. It sends continuous or pulsed microwave energy to the surrounding space. When the microwave encounters the target object, it is reflected. The radar receiving system captures the echo signal and changes it according to the arrival time and amplitude of the signal. Determine the distance, bearing and speed of the target. The wavelength of microwave radar is much larger than that of laser, causing its resolution and penetration characteristics to be different from lidar.

resolution
LiDAR has extremely high resolution, including distance, angle and speed resolution, and can accurately distinguish very close objects and depict details at the level of several centimeters, making it suitable for areas such as autonomous driving.
The resolution of microwave radar is relatively low, especially the early microwave radar was mainly used for long-distance detection and large-scale coverage. However, with the advancement of technology, its resolution has been improved, but it is still not as good as lidar.
Penetration and weather adaptability
Microwave radar has strong penetrability and can maintain good detection results especially in bad weather. It is suitable for aviation, navigation and other fields.
Lidar will be greatly affected when encountering water droplets, haze, etc., but it has excellent detection performance in clear environments.
Anti-interference and concealment
Due to its short wavelength, lidar has less interference from natural background radiation and has strong anti-reconnaissance capabilities.
Microwave radar may be interfered by radio signals, but the universality of its band gives it a certain ability to resist interference.
Differences in application scenarios
Applications of lidar
Lidar is widely used in fields such as unmanned driving, three-dimensional terrain surveying and construction planning, and has become a key sensor for advanced autonomous driving systems.
Microwave Radar Applications
Microwave radar is widely used in weather forecasting, aviation navigation, automobile safety functions and other fields. Particularly in the area of vehicle safety, millimeter wave radar is becoming more and more common.
LiDAR and microwave radar have their own characteristics in terms of principles, performance and application fields, and each has its own advantages and disadvantages. In practical applications, it is often necessary to comprehensively consider their advantages and disadvantages and select appropriate radar technology to meet different needs.
Related Information
-
-
Phone
+86 135 3401 3447 -
Whatsapp





