Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase Inverters: Pros and Cons
2024/8/17 9:40:03
Views:
Inverters are basic gadgets within the field of control gadgets, capable for changing over coordinate current (DC) into substituting current (AC). Common sorts of inverters incorporate single-phase and three-phase inverters, each with unmistakable characteristics in terms of working standards, application scenarios, and execution. This article will briefly analyze their structure, standards, applications, and focal points and impediments.
Overview of Single-Phase Inverters

Single-phase Inverter
Application Scenario Analysis
Single-phase inverters are broadly utilized in control frameworks such as UPS control supplies, particularly playing a key part in sun oriented control era frameworks. Photovoltaic boards change over sun powered vitality into coordinate current through a photovoltaic inverter, and after that the single-phase inverter changes over this coordinate current into rotating current for family utilize. In domestic UPS control supplies, the single-phase inverter changes over coordinate current into the rotating current required by the stack, guaranteeing the ordinary operation of family apparatuses.
Advantages and Disadvantages Analysis
Single-phase inverters have significant advantages due to their simple structure, low cost, and ease of installation and maintenance. Their output is single-phase AC, making them particularly suitable for integration with household power systems, thus being widely used in the residential sector. However, single-phase inverters also have limitations, such as only outputting single-phase AC, making them less suitable for large-scale applications in industrial environments that require three-phase power. Additionally, the energy conversion process has lower efficiency, resulting in a certain degree of energy loss.
Definition and Working Principle
A single-phase inverter could be a gadget that changes over a single-phase control source (such as 220V AC utilized in families) into coordinate current and encourage changes over the coordinate current into rotating current. Its working principle includes filtering the direct current and inputting it into the inverter in the AC circuit. Through the control of the switching tubes, the required alternating current is output, achieving the conversion from direct current to alternating current.
Overview of Three-Phase Inverters

Three-phase Inverter
Definition and Working Principle
A three-phase inverter could be a control transformation gadget that changes over coordinate current into three-phase rotating current. Through the combination of input channels, rectifiers, middle of the road DC joins, inverters, and yield channels, the three-phase inverter can change over DC control sources such as sun oriented vitality and wind vitality into AC control for family or mechanical utilize, and it can give a high-quality yield voltage waveform.
Application Situation Examination
Three-phase inverters are broadly utilized in renewable vitality era areas (such as sun powered and wind control era) and play a key part in mechanical events that require three-phase control, such as engine drives and control transmission. Since three-phase inverters can yield three-phase AC, they have more grounded control supply capabilities and higher soundness, successfully assembly the strict prerequisites of the mechanical division for high-quality electrical vitality.
Advantages and Disadvantages Analysis
Three-phase inverters have the advantages of outputting three-phase AC, strong power supply capabilities, high efficiency, and low energy conversion loss, and they are also relatively easy to operate and maintain. However, three-phase inverters are more expensive, have a more complex structure, and are limited in certain single-phase load applications.
Differences Between Single-Phase and Three-Phase Inverters
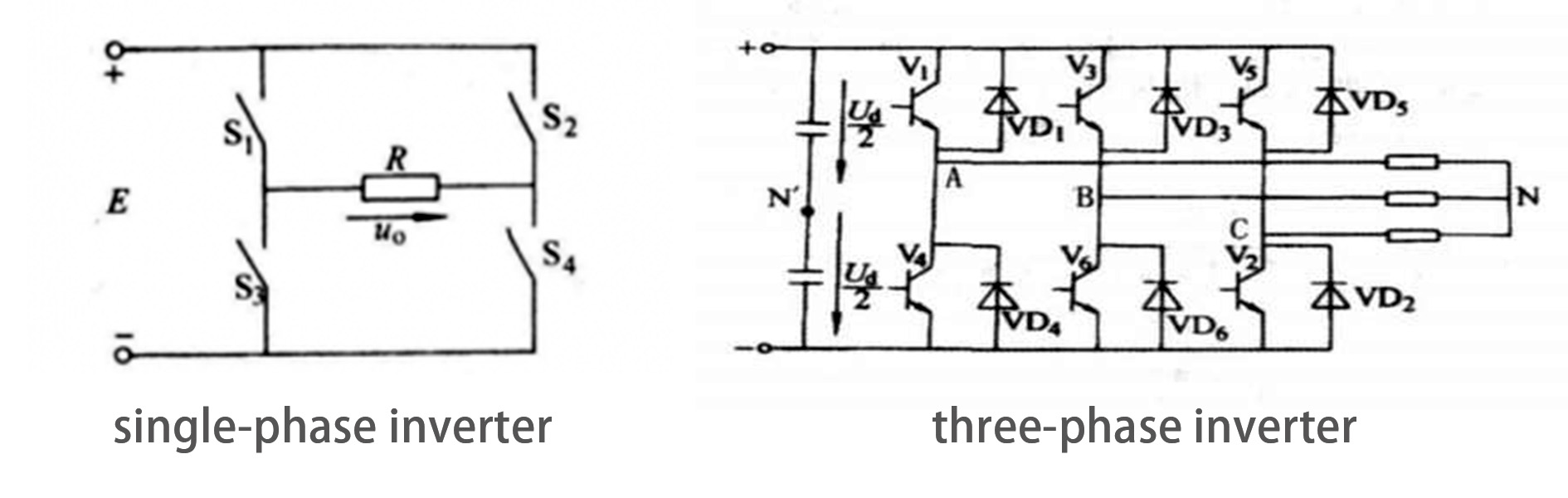
Single-phase Inverter and Three-phase Inverter
Structural comparison
The plan of single-phase inverters is generally straightforward, ordinarily comprising of fundamental components such as a channel circuit, an inverter circuit, and an yield circuit. In differentiate, three-phase inverters are more complex, with structures that ordinarily incorporate input channels, rectifiers, middle DC joins, inverters, and yield channels. This multi-layered plan makes three-phase inverters more practically total but too increments their complexity.
Yield Characteristics Contrasts
Single-phase inverters yield single-phase AC, with as it were one voltage and current waveform. In differentiate, three-phase inverters yield three-phase AC, giving three free and equally dispersed current waveforms, with higher waveform quality, making them reasonable for applications with higher control quality prerequisites.
Application Situation Contrasts
Single-phase inverters are primarily utilized in family control supplies and UPS control supplies for single-phase stack applications, whereas three-phase inverters are broadly utilized in mechanical areas requiring three-phase control, such as renewable vitality era, engine drives, and control transmission.
Conclusion
There are critical contrasts between single-phase and three-phase inverters in terms of structure, yield characteristics, application scenarios, and execution. In down to earth applications, it is significant to select the fitting sort of inverter based on particular needs. As control hardware innovation propels, the execution of inverters will proceed to move forward, and their application scenarios will ended up more broad.
Related Information
-
-
Phone
+86 135 3401 3447 -
Whatsapp





