Diversified uses of graphite electrodes
2024/4/29 15:13:07
Views:
Graphite electrodes are primarily used in industries such as metallurgy and chemical engineering, with specific applications outlined as follows:
1. Metallurgical Sector:
Steelmaking in an electric arc furnace (EAF) requires graphite electrodes as a necessary component. In China, EAF steel production accounts for approximately 18% of crude steel production, with graphite electrodes comprising 70% to 80% of the total usage. EAF steelmaking involves the introduction of electrical current through graphite electrodes into the furnace, utilizing the high-temperature heat generated by the electric arc for smelting.
 2. Chemical Engineering Sector:
2. Chemical Engineering Sector:
Graphite electrodes find extensive use in mineral thermal furnaces, particularly in the production of industrial silicon and yellow phosphorus. These furnaces utilize buried electrodes to generate arcs within the charge material, utilizing the heat generated by resistance to facilitate material heating. The demand for graphite electrodes in mineral thermal furnaces is substantial, with approximately 100 kilograms required for every ton of silicon produced and about 40 kilograms for every ton of yellow phosphorus.
Graphite electrodes are a type of high-temperature-resistant graphite conductive material, categorized into various types including regular power (RP), high power (HP), semi-ultra high power (SHP), and ultra-high power (UHP).
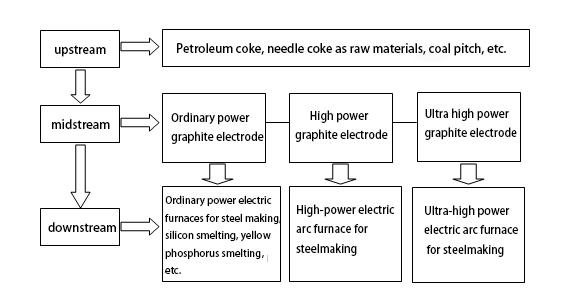 3. Application in Electric Arc Furnaces (EAFs):
3. Application in Electric Arc Furnaces (EAFs):
Graphite electrode materials are employed in electric arc furnace steelmaking. In this process, graphite electrodes introduce working current into the furnace, utilizing the heat generated by the electric arc for smelting. Graphite electrodes account for approximately 70% to 80% of China's total graphite electrode consumption in steelmaking.
4. Application in Mineral Thermal Furnaces:
These electrodes are used in the production of ferroalloys, pure silicon, yellow phosphorus, calcium carbide, and other products. The electrodes buried within the charge material generate arcs, and the current passing through the charge material produces heat.
5. Application in Resistance Furnaces:
Graphite electrodes are used in the production of graphite products, glass melting kilns, and silicon carbide electric furnaces, among others.
6. Other Applications:
Large quantities of graphite electrode blanks are also processed into various shaped products such as crucibles, graphite boats, hot-pressed molds, and heating elements for vacuum furnaces.
It is worth noting that in high-temperature composite materials such as graphite electrodes, graphite is susceptible to oxidation and combustion reactions at high temperatures, increasing the porosity and loose structure of the carbon layer on the surface.
Graphite electrodes, made from petroleum coke, asphalt coke, and coal tar pitch, serve as high-temperature-resistant graphite conductive materials for heating and smelting furnace materials.
As vital carbon products, graphite electrodes play essential roles in conducting electricity and heat transfer in equipment such as arc furnaces, mineral thermal furnaces, electric furnaces, and resistance furnaces.
The performance of graphite electrodes includes conductivity, high-temperature resistance, thermal shock resistance, oxidation resistance, and mechanical strength. Their excellent conductivity effectively transfers current and generates high-temperature arcs, while their high-temperature resistance allows for long-term stable operation.
Graphite electrodes have wide-ranging applications, primarily in smelting equipment such as electric arc furnaces, mineral thermal furnaces, electric furnaces, and resistance furnaces. Their performance directly impacts the efficiency and effectiveness of smelting equipment. Therefore, careful consideration of performance indicators and attention to maintenance and upkeep are necessary to prolong their lifespan and enhance their effectiveness.
In conclusion, graphite electrodes hold significant promise for various industries including metallurgy, chemical engineering, mechanical engineering, electronics, and more. As technology advances, the performance and applications of graphite electrodes will continue to improve, making substantial contributions to industrial development.
1. Metallurgical Sector:
Steelmaking in an electric arc furnace (EAF) requires graphite electrodes as a necessary component. In China, EAF steel production accounts for approximately 18% of crude steel production, with graphite electrodes comprising 70% to 80% of the total usage. EAF steelmaking involves the introduction of electrical current through graphite electrodes into the furnace, utilizing the high-temperature heat generated by the electric arc for smelting.

Graphite electrodes find extensive use in mineral thermal furnaces, particularly in the production of industrial silicon and yellow phosphorus. These furnaces utilize buried electrodes to generate arcs within the charge material, utilizing the heat generated by resistance to facilitate material heating. The demand for graphite electrodes in mineral thermal furnaces is substantial, with approximately 100 kilograms required for every ton of silicon produced and about 40 kilograms for every ton of yellow phosphorus.
Graphite electrode materials are employed in electric arc furnace steelmaking. In this process, graphite electrodes introduce working current into the furnace, utilizing the heat generated by the electric arc for smelting. Graphite electrodes account for approximately 70% to 80% of China's total graphite electrode consumption in steelmaking.
4. Application in Mineral Thermal Furnaces:
These electrodes are used in the production of ferroalloys, pure silicon, yellow phosphorus, calcium carbide, and other products. The electrodes buried within the charge material generate arcs, and the current passing through the charge material produces heat.
5. Application in Resistance Furnaces:
Graphite electrodes are used in the production of graphite products, glass melting kilns, and silicon carbide electric furnaces, among others.
6. Other Applications:
Large quantities of graphite electrode blanks are also processed into various shaped products such as crucibles, graphite boats, hot-pressed molds, and heating elements for vacuum furnaces.
It is worth noting that in high-temperature composite materials such as graphite electrodes, graphite is susceptible to oxidation and combustion reactions at high temperatures, increasing the porosity and loose structure of the carbon layer on the surface.
Graphite electrodes, made from petroleum coke, asphalt coke, and coal tar pitch, serve as high-temperature-resistant graphite conductive materials for heating and smelting furnace materials.
As vital carbon products, graphite electrodes play essential roles in conducting electricity and heat transfer in equipment such as arc furnaces, mineral thermal furnaces, electric furnaces, and resistance furnaces.
The performance of graphite electrodes includes conductivity, high-temperature resistance, thermal shock resistance, oxidation resistance, and mechanical strength. Their excellent conductivity effectively transfers current and generates high-temperature arcs, while their high-temperature resistance allows for long-term stable operation.
Graphite electrodes have wide-ranging applications, primarily in smelting equipment such as electric arc furnaces, mineral thermal furnaces, electric furnaces, and resistance furnaces. Their performance directly impacts the efficiency and effectiveness of smelting equipment. Therefore, careful consideration of performance indicators and attention to maintenance and upkeep are necessary to prolong their lifespan and enhance their effectiveness.
In conclusion, graphite electrodes hold significant promise for various industries including metallurgy, chemical engineering, mechanical engineering, electronics, and more. As technology advances, the performance and applications of graphite electrodes will continue to improve, making substantial contributions to industrial development.
Related Information
-
-
Phone
+86 135 3401 3447 -
Whatsapp





