Full-Bridge Driver in Modern Motor Control
2024/7/26 16:15:22
Views:
Full bridge drivers, commonly referred to as H-bridge drivers, are widely used control devices in electrical and electronic engineering. They play a crucial role in motor control, robotics, electric vehicles, DC converters, and other fields. By regulating the speed and direction of electric motors or other loads, full bridge drivers enable precise control of motors, providing efficient solutions for various applications.
Applications of Full Bridge Drivers
Full bridge drivers are widely used in several fields, including but not limited to:
1. Electric Vehicles: Control the motors of electric vehicles, achieving power transmission and speed control.
2. Mechanical autonomy:Control the engines of robots, empowering exact development and pose control.
3. Family Apparatuses:Broadly utilized within the control of DC engines in family apparatuses, such as washing machines and vacuum cleaners.
4. Mechanical Computerization:Control engines in mechanical gear, accomplishing exact position and speed control.
5. Sun based Following Frameworks:Control the introduction of sun oriented boards in photovoltaic frameworks to maximize sun powered vitality capture.
Working Mechanism of Full Bridge Drivers
The working principles of full bridge drivers are as follows:
1. Logic gates generate corresponding pin signals based on control signals.
2. Drivers control the conduction state of electronic switches based on pin signals.
3. The conduction state of the switches determines the motor's operating direction and speed.
4. Feedback circuits monitor motor speed and current to achieve closed-loop control.
By precisely controlling motor start, stop, forward and reverse rotation, and speed adjustment, full bridge drivers provide efficient motor control solutions for various applications.
Principles of Full Bridge Drivers
Full bridge drivers control the extremity and size of the yield voltage by opportune exchanging four switches, in this way controlling the motor's heading and speed. When the two inclining switches are at the same time on, current streams through the stack, causing the engine to turn in one heading; when the other two corner to corner switches are on, the current streams within the inverse heading, causing the engine to turn in invert. By changing the switch states, the engine can switch between distinctive speeds and headings.
Structure of Full Bridge Drivers
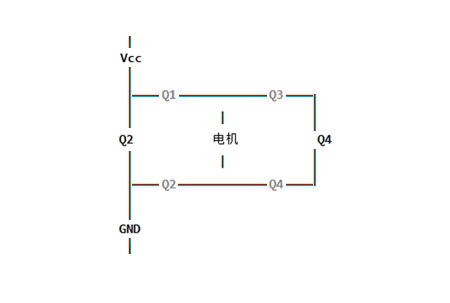
Structure of Full Bridge Drivers
Full bridge drivers typically consist of the following key parts:
1. Four electronic switches: Located in the four branches of the H-bridge, responsible for controlling the current direction.
2. Motor interface: Connects the motor and the full bridge driver, transmitting control signals and power.
3. Control circuit: Includes logic gates, drivers, and feedback circuits, processing input signals and generating switch control signals.
4. Power interface: Provides necessary power supply for the full bridge driver and the motor.
These components work together to achieve precise control of the motor, making full bridge drivers play an important role in various applications.
Related Information
-
-
Phone
+86 135 3401 3447 -
Whatsapp





