Types, Symbols, and Applications of Diodes
2024/11/14 11:23:43
Views:
what is a diode and how it works
- What is a Diode?
- Characteristics of Diode
- Types of Diodes and their Symbols
- Diode Application Circuit
- How to Test a Diode
What is a Diode?
A diode is a semiconductor composed of a PN junction with the function of conducting in one direction. If you apply a forward voltage to both ends of the diode, it will conduct. If you apply a reverse voltage to the diode, it will be cut off.
Forward conduction

When the anode of the diode is connected to the positive terminal of the power supply, current flows through the diode, and the LED lights up.
Reverse cutoff

When the cathode of the diode is connected to the positive terminal of the power supply, the diode is in cutoff, and the LED does not light up.
Characteristics of Diode
● Forward voltage drop:When a diode conducts in the forward direction, the voltage drop across its two terminals is approximately 0.7V. If the supply voltage is lower than 0.7V, the current cannot pass through and the diode cannot conduct.
● Reverse breakdown voltage:Different models of diodes have different rated breakdown voltages. If the reverse voltage applied to the diode exceeds its rated breakdown voltage, the reverse current of the diode will sharply increase, causing the diode to break down. Generally, diode breakdown is not recoverable (except for Zener diodes).

From the diagram, it can be observed that the forward characteristics are as follows: when the forward voltage is less than the threshold voltage, the diode does not conduct. Once the forward voltage exceeds the threshold voltage, the diode begins to conduct with a weak current. If the current continues to increase, the voltage drop across the diode will slightly increase.
As for the reverse characteristics: when the reverse voltage is below the VBR value, there is almost no reverse leakage current. However, when the reverse voltage exceeds the VBR value, the reverse leakage current increases sharply, and the diode enters the breakdown state.
Types of Diodes and their Symbols

Photodiode: Converts light signals into current,mainly used in optical sensors and optical communication devices.
LED (Light-emitting Diode): It's the kind of light-emitting indicator you often see (LED lights).
Zener Diode: Commonly used in voltage regulation circuits, it operates in the breakdown state and is recoverable.
Rectifier Diode: You can use it to change AC voltage into pulsating DC voltage, and commonly used in rectifier circuits.
Schottky Diode: The forward voltage drop is relatively low, and the reverse recovery time is very fast, commonly used in circuits with low power consumption requirements and relatively fast switching frequencies.
Transient Voltage Suppression (TVS) Diode: It can be used to protect circuits from the impact of surge current, and it also works in the breakdown state, able to absorb the instantaneous high-power surges to the ground and react quickly.
Thyristor Diode (SCR): It is commonly used in high-power circuits that need to be controlled. After giving the turn-on signal and then removing it, the circuit can maintain its conducting state.
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Diode: Used to protect sensitive electronic components from electrostatic discharge damage, with fast response (The symbol is the same as the TVS diode symbol).
Rectifier Bridge: Consists of four diodes that you can used to convert AC to DC, widely used in power supply rectifier circuits.
Diode Application Circuit
Rectifier Circuit: Converts AC into one-way pulsating DC is the rectifier circuit, and it is mainly composed of rectifier diodes.

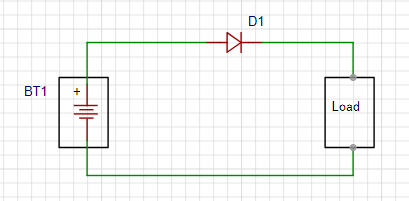
Reverse Polarity Protection: In a circuit, connecting a diode in series can effectively prevent damage to circuit components caused by the reversal of power supply polarity. This circuit is simple and easy to implement. The drawback is that if the power supply polarity is reversed, the circuit will stop working entirely.
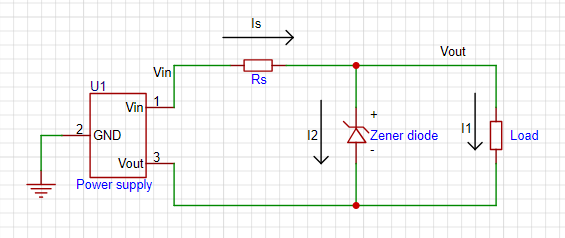
Voltage Regulation Circuit: The voltage regulation circuit consists of a Zener diode and a resistor (RS), which can help you stabilize the voltage across the load within a rated voltage range (changes in the power supply voltage will not affect the constant voltage at both ends of the load).
Freewheeling Circuit: Diode D18 plays a continuation role in the circuit:When the power supply is on, and current flows through the coil towards transistor Q10, diode D18 is in cutoff. At the moment the power supply is turned off-the coil generates an electromotive force-creating an inertia current (with a relatively high instantaneous voltage)--At this time, the potential of point b is higher than point a,the 1N4148 diode conducts and forms a loop with the coil, consuming the energy of the coil.

Voltage Doubler Circuit: When the negative half cycle, the peak voltage value through D1 stored in C1 positive terminal,positive half cycle, the power supply voltage and the voltage stored in C1 positive terminal superposition to charge C2, making C2 positive terminal and load voltage are equal to twice the power supply voltage.

Clamping Circuit: Using two 1N4148 diodes to protect the circuit, when the ADC in voltage is higher than 3.3V, diode D35 conducts, stabilizing the voltage at 3.3V. When the ADC in voltage is negative, diode D24 conducts, stabilizing the voltage at 0V.

Envelope Circuit: This circuit, due to the combination of the diode and capacitor, can capture the peak value of the input signal, so it can be used as a peak detection circuit,and can also be used for envelope circuit.

How to Test a Diode
You can use a multimeter to test the diode

To test the forward voltage drop of the diode, you need to connect the red probe to the anode of the diode. If the voltage of 0.5-0.7V is displayed, it means that the diode is normal.

To test the reverse cutoff of the diode, you need to connect the red probe to the cathode of the diode. If it shows 0.0LV, it means that the diode is normal.
In the future, with the development of semiconductor technology, diodes will become more energy-efficient, with increasingly lower voltage drops, higher reverse breakdown voltages, and improved temperature resistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How does a diode work?
A diode Working principle permits current to flow only in the forward direction (when forward biased) and blocks current in the reverse direction (when reverse biased).
2. What are light-emitting diodes made of?
Made from semiconductor materials such as gallium arsenide or gallium nitride.
3. Do diodes have resistance?
Yes, Diodes have a small forward resistance when forward biased.
4. What does a diode do?
The diode controls the direction of the current so that it flows in only one direction and prevents the reverse flow.
5. How to connect a diode?
Connect the anode to the positive side and the cathode to the negative side for forward bias.
6. How many diodes are used in a bridge rectifier?
Four diodes.
7. How to install a diode?
Install the diode so that the anode (marked side) connects to the positive voltage and the cathode (unmarked side) connects to the negative voltage
8. Where to buy diodes?
Diodes can be purchased from electronics stores, online retailers like icwhale.com,Amazon, Digi-Key, or Mouser Electronics.
Related Information
-
-
Phone
+86 135 3401 3447 -
Whatsapp





