Selection of DCDC Converter Topologies in Power Supply Design
2024/7/29 14:18:40
Views:
DC/DC converters are fundamental components in cutting edge electronic gadgets, utilized to change over one DC voltage to another. Diverse topologies offer particular points of interest and impediments depending on the application, making the choice of an fitting topology vital. This article investigates a few common DC/DC converter topologies, counting their working standards, application scenarios, and variables to consider when selecting them.
1. Buck Converter (Step-Down Converter)
This topology is utilized to step down the input voltage to a lower yield voltage, commonly found in gadgets like phone chargers and tablet control supplies. The Buck converter employments a combination of a switch and an inductor to store and discharge vitality, accomplishing voltage diminishment.
2. Boost Converter (Step-Up Converter)
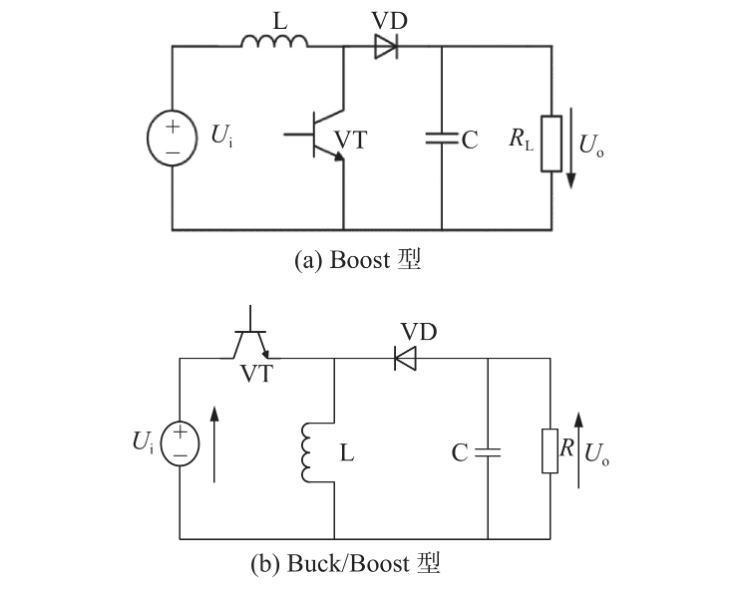
The Boost converter increments the input moo voltage to the next yield voltage, appropriate for applications requiring tall voltage yield such as Driven drivers and sun powered boards. It uses inductor energy storage and switch control to boost the voltage.
3. Buck-Boost Converter
The Buck-Boost converter can adaptably step up or step down the input voltage to the required yield voltage, perfect for applications with shifting voltage ranges like electric vehicle control administration.
It offers high efficiency and stable output voltage across a wide range.
4. Flyback Converter
The Flyback converter is commonly used in applications requiring electrical isolation, such as power adapters and LED lighting. It uses a transformer to provide isolation and voltage conversion, suitable for low-power applications, though with relatively lower efficiency.
5. Half-Bridge Converter
The Half-Bridge converter consists of two switches and is suited for medium to high-power applications. It effectively reduces output voltage fluctuations and is commonly used in high-performance power systems.
1. Input and Output Voltage Range
Determining the input and output voltage ranges is fundamental in selecting the appropriate topology. For example, Buck converters are suitable for step-down applications, Boost converters for step-up needs, and Buck-Boost converters for unstable voltage scenarios.
2. Conversion Efficiency
High-efficiency converters decrease vitality misfortune and warm era, subsequently upgrading generally framework execution and unwavering quality. Topologies with high conversion efficiency should be prioritized.
3. Cost and Reliability
Design cost and system reliability are important considerations. Distinctive topologies have shifting costs and unwavering quality, which got to be adjusted based on genuine prerequisites.
4. Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
EMC is pivotal for the right working of the framework.
Different topologies have varying impacts on electromagnetic interference, so selecting a structure with minimal EMC effects is necessary.
5. Warm Administration and Bundling
Warm administration is basic in high-power applications. Distinctive topologies have distinctive warm administration needs, requiring cautious thought of bundling and cooling necessities.
1. Utilize of High-Efficiency Materials
Unused semiconductor materials like Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) will upgrade converter proficiency and exchanging speed, diminishing vitality misfortune.
2. Intelligent Control
Integrated digital control in DC/DC converters will enable more precise voltage and current regulation, along with self-protection and fault detection features.
3. Modular Design
Modular design allows for easy integration and maintenance of converters, with flexible expansion based on specific needs.
1. Diagram of DC/DC Converter Topologies
DC/DC converter topologies are differing, with common sorts counting Buck, Boost, Buck-Boost, Flyback, Half-Bridge, and Push-Pull. Each topology has one of a kind characteristics in terms of vitality transformation proficiency, fetched, unwavering quality, electromagnetic compatibility, and warm execution.1. Buck Converter (Step-Down Converter)
This topology is utilized to step down the input voltage to a lower yield voltage, commonly found in gadgets like phone chargers and tablet control supplies. The Buck converter employments a combination of a switch and an inductor to store and discharge vitality, accomplishing voltage diminishment.
2. Boost Converter (Step-Up Converter)
The Boost converter increments the input moo voltage to the next yield voltage, appropriate for applications requiring tall voltage yield such as Driven drivers and sun powered boards. It uses inductor energy storage and switch control to boost the voltage.
3. Buck-Boost Converter
The Buck-Boost converter can adaptably step up or step down the input voltage to the required yield voltage, perfect for applications with shifting voltage ranges like electric vehicle control administration.
It offers high efficiency and stable output voltage across a wide range.
4. Flyback Converter
The Flyback converter is commonly used in applications requiring electrical isolation, such as power adapters and LED lighting. It uses a transformer to provide isolation and voltage conversion, suitable for low-power applications, though with relatively lower efficiency.
5. Half-Bridge Converter
The Half-Bridge converter consists of two switches and is suited for medium to high-power applications. It effectively reduces output voltage fluctuations and is commonly used in high-performance power systems.

2. Criteria for Selecting DC/DC Converter Topologies
When choosing a suitable DC/DC converter topology, several factors need to be considered:1. Input and Output Voltage Range
Determining the input and output voltage ranges is fundamental in selecting the appropriate topology. For example, Buck converters are suitable for step-down applications, Boost converters for step-up needs, and Buck-Boost converters for unstable voltage scenarios.
2. Conversion Efficiency
High-efficiency converters decrease vitality misfortune and warm era, subsequently upgrading generally framework execution and unwavering quality. Topologies with high conversion efficiency should be prioritized.
3. Cost and Reliability
Design cost and system reliability are important considerations. Distinctive topologies have shifting costs and unwavering quality, which got to be adjusted based on genuine prerequisites.
4. Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
EMC is pivotal for the right working of the framework.
Different topologies have varying impacts on electromagnetic interference, so selecting a structure with minimal EMC effects is necessary.
5. Warm Administration and Bundling
Warm administration is basic in high-power applications. Distinctive topologies have distinctive warm administration needs, requiring cautious thought of bundling and cooling necessities.
3. Future Trends
As technology advances, DC/DC converter design is also evolving. Future trends include:1. Utilize of High-Efficiency Materials
Unused semiconductor materials like Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) will upgrade converter proficiency and exchanging speed, diminishing vitality misfortune.
2. Intelligent Control
Integrated digital control in DC/DC converters will enable more precise voltage and current regulation, along with self-protection and fault detection features.
3. Modular Design
Modular design allows for easy integration and maintenance of converters, with flexible expansion based on specific needs.
4. High Power DensityAs devices become smaller, high power density designs for DC/DC converters will become more important, requiring optimization of layout and thermal management to achieve higher power output in smaller volumes.
In rundown, selecting the fitting DC/DC converter topology requires a comprehensive thought of voltage necessities, change productivity, fetched, unwavering quality, electromagnetic compatibility, and warm administration. With mechanical headways, DC/DC converters will proceed to advance in effectiveness, insights, and seclusion, giving more proficient and solid control arrangements for different applications.Related Information
-
-
Phone
+86 135 3401 3447 -
Whatsapp





