Basic elements and functional analysis of control circuits
2024/7/27 17:09:04
Views:
Control circuits are circuit systems formed by connecting electrical or electronic components, used to monitor, adjust, protect, or operate electrical equipment, mechanical equipment, or systems. They can receive input signals, process control logic, and generate output signals to manipulate the operation of equipment. Control circuits play a crucial role in the field of industrial control, helping to achieve automated production and operation.
Functions of Control Circuits
The most capacities of control circuits incorporate but are not restricted to the taking after:
Flag Transmission:Transmitting different signals (such as analog signals, advanced signals) to diverse components.
Rationale Control:Making coherent judgments based on preset conditions to control the operational states of gear, such as beginning and ceasing, speed, and course.
Over-burden Security:Recognizing the working status of hardware, consequently cutting off the control supply when it surpasses the appraised stack or is unusual, ensuring the hardware from harm.
Blame Determination:Checking the operational status of gear, convenient recognizing issues and giving alerts or prompts.
Remote Control: Monitoring and operating equipment through the network or remote devices.
Automated Control: Achieving automated operation of equipment to improve production efficiency and precision.
Components of Control Circuits
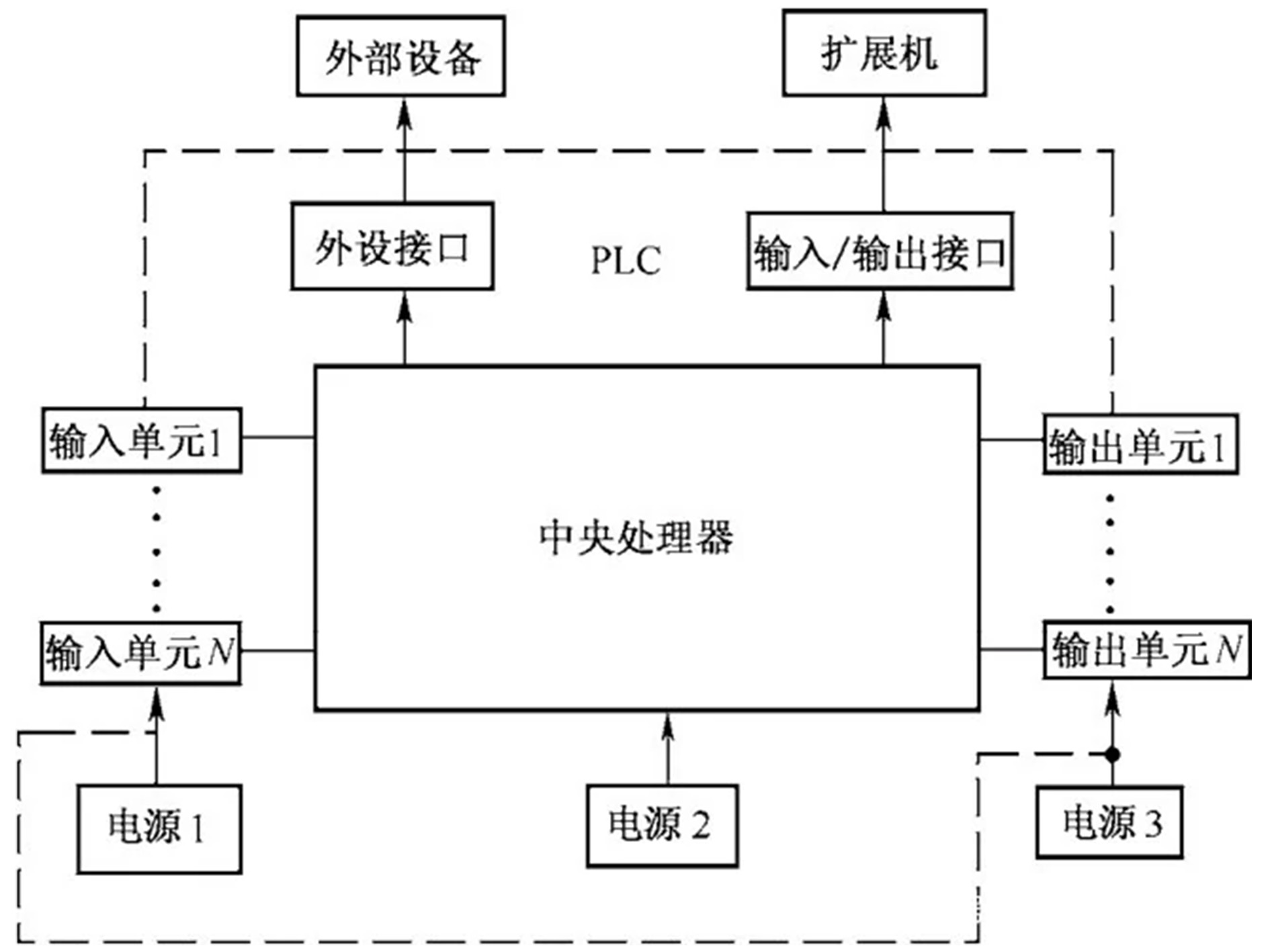
Components of Control Circuits
Control circuits usually consist of the following basic elements:
Input Module: Used to receive external signals, such as sensor signals, switch signals, etc.
Controller:The central preparing unit, mindful for handling input signals, executing control rationale, and producing yield signals.
Yield Module:Changes over the signals yield by the controller into shapes that can control actuators (such as engines, valves, etc.).
Actuator: Executes corresponding actions based on output signals to control equipment or systems.
Types of Control Circuits
Control circuits can be divided into various types based on their functions and characteristics, including:
Switch Control Circuits: Controlling the start, stop, direction, etc., of equipment based on switch signals.
Logic Control Circuits: Implementing logical judgment and control based on components like logic gates and triggers.
Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) Control Circuits:Utilizing PID calculations to realize exact control of gear parameters.
Timing Control Circuits: Achieving timed control functions of equipment based on time parameters.
Analog Control Circuits: Using analog signals to control the operational state of equipment.
PLC Control Circuits: Implementing complex control functions and automated operations based on programmable logic controllers (PLC).
In industrial control, control circuits play roles such as signal transmission, logical judgment, overload protection, fault diagnosis, remote monitoring, and automated control, ensuring efficient and safe operation of equipment and systems. By receiving signals through input modules, processing and generating output signals by controllers, and ultimately realizing the control of equipment through output modules and actuators, this systematic and automated control method greatly improves production efficiency and precision, enabling the smooth realization of modern industrial control.
Related Information
-
-
Phone
+86 135 3401 3447 -
Whatsapp





